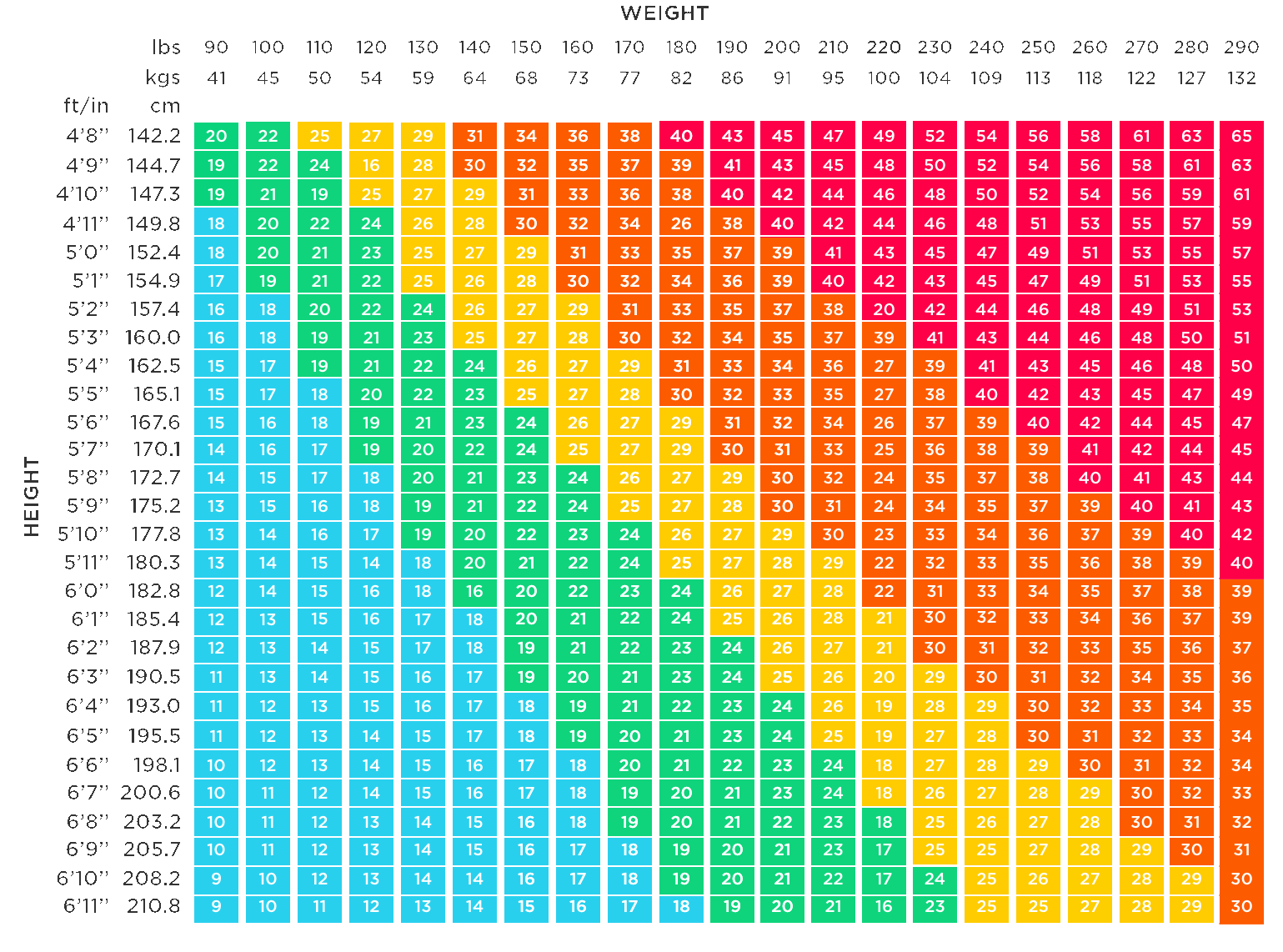
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used measurement that helps to determine whether a person has a healthy body weight or not. It is a simple calculation that takes into account a person’s height and weight. By understanding and calculating BMI, individuals can assess whether they are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese, which in turn can provide valuable insights into their overall health and well-being.
Calculating BMI Formula
The formula for calculating BMI is relatively straightforward. It is obtained by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters.
BMI Calculation Formula:
BMI = weight (kg) / (height (m))^2
Interpreting BMI Results
BMI values can be interpreted using different ranges established by health organizations and professionals. Typically, the following categories are considered:
Underweight: A BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight. This might indicate possible malnutrition or other health concerns. Individuals falling in this category should consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and advice.
Normal Weight: A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered normal weight. This range indicates a healthy weight for most individuals. However, it is still important to focus on other aspects of health like nutrition, physical activity, and overall well-being.
Overweight: Individuals with a BMI between 25 and 29.9 are considered overweight. This may be an indication of excess body fat, which can increase the risk of various health conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. Maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise can help reduce the risk.
Obese: A BMI of 30 or higher is classified as obese. Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing serious health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and certain types of cancer. Seeking professional guidance to manage weight is crucial in such cases.
The Limitations of BMI
While BMI is a valuable tool for assessing body weight on a population level, it does have some limitations when it comes to individuals. This measurement does not consider factors such as body composition, muscle mass, and distribution of fat, which can vary significantly from person to person. Therefore, it is essential to approach BMI as a screening tool and not the sole determinant of an individual’s overall health status.
Factors influencing BMI accuracy:
Lean Muscle Mass: Athletes or individuals with a higher amount of lean muscle mass may have a higher BMI, which does not necessarily indicate that they are overweight or unhealthy.
Body Composition: BMI does not differentiate between fat and muscle. Therefore, individuals with higher muscle mass may have a higher BMI, even if their body fat percentage is in a healthy range.
Ethnicity and Genetic Variations: Different ethnic groups may have variations in body composition and fat distribution, which can affect the interpretation of BMI.
Age and Gender: BMI standards for children, teenagers, and the elderly may differ due to variations in growth patterns, hormonal changes, and overall body development.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Evaluation
While BMI is a useful tool, it is important to remember that it is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to assessing overall health. Other factors such as waist circumference, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and family medical history should also be taken into consideration.
It is recommended to have regular check-ups with healthcare professionals who can provide a holistic assessment of your health, including BMI evaluation, and offer guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle.