In today’s fast-paced world, where convenience foods are abundant, it is essential to make informed choices about
the food we consume. One way to do this is by carefully reading food labels. Food labels provide vital information
about the nutritional content, ingredients, and potential allergens in a product. By understanding how to decode
these labels, you can make better choices for your health and well-being.
The Importance of Food Labels
Food labels play a crucial role in helping consumers make informed decisions about the products they purchase.
These labels provide information about the serving size, calories, macronutrients (such as fat, protein, and
carbohydrates), vitamins, minerals, and often highlight potential allergens. By reading food labels, you can
determine if a particular product aligns with your dietary needs and goals.
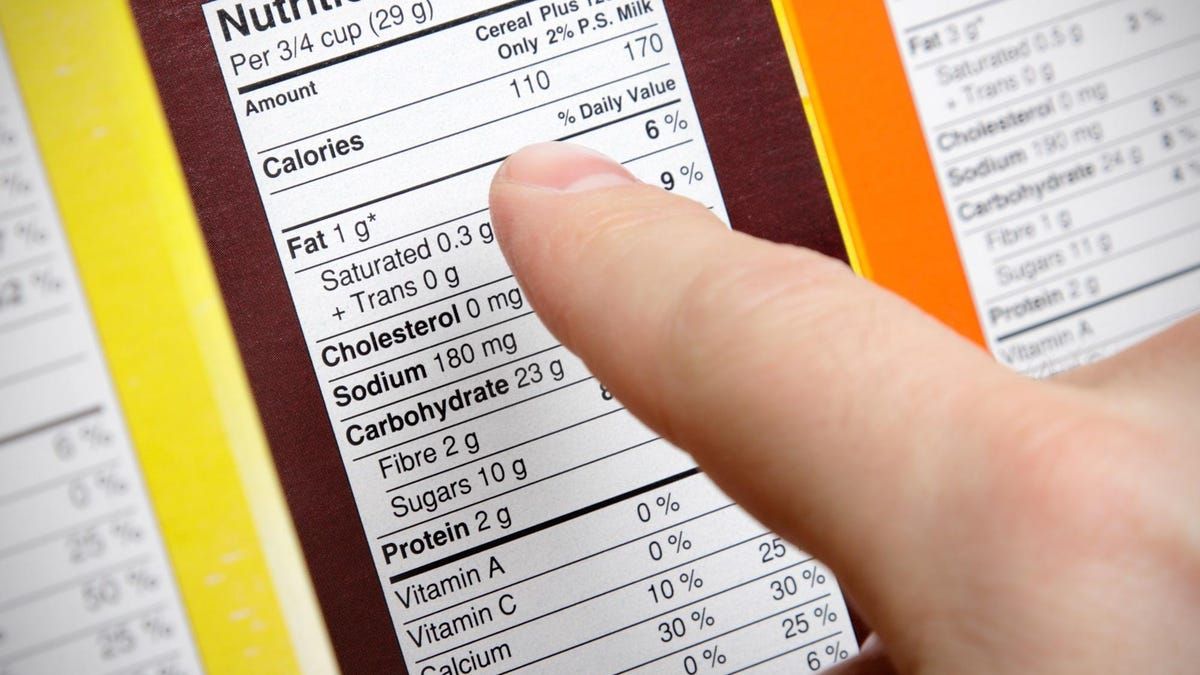
Decoding the Nutrition Facts
One of the primary sections of a food label is the “Nutrition Facts” panel. This panel provides detailed
information about the product’s nutritional content. It includes information on serving size, calories, fat
content (including saturated and trans fat), cholesterol, sodium, carbohydrates, fiber, sugar, and protein.
Additionally, it may indicate the presence of certain essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, iron,
and calcium. Understanding these values is crucial as they help you monitor your calorie intake and make healthier
choices.
Pay Attention to Serving Sizes
Serving sizes on food labels require careful consideration. Often, a package may contain multiple servings, which
means that the nutritional values listed on the label are per serving, not for the entire package. Be mindful of
how much you consume, as it may significantly impact your overall nutrient intake. If you eat two servings of a
product, be sure to double the values mentioned on the label.
Understanding Percent Daily Value (%DV)
The %DV listed on food labels is a reference value based on a 2,000-calorie diet. It represents the proportion of
each nutrient in a serving size, relative to the recommended daily intake. For example, if a food item has 15% DV
for iron, it means that one serving provides 15% of the iron you need in a day. This percentage can help you
evaluate whether a particular food is high or low in a specific nutrient. A good rule of thumb is that 5% or less
is considered low, while 20% or more is considered high.
Spotting Hidden Sugars and Unhealthy Fats
Food labels can reveal hidden sugars and unhealthy fats that may be present in a product. Be cautious of terms
such as high fructose corn syrup, dextrose, maltose, and sucrose, as these indicate added sugars. Added sugars can
contribute to weight gain, diabetes, and other health-related issues. Moreover, trans fats and saturated fats can
raise the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Opt for products with low levels of these fats to make healthier
choices.
Deciphering Ingredient Lists
Another crucial section of food labels is the ingredient list. Ingredients are listed in descending order by
weight, with the most abundant ingredient listed first. Pay attention to the first few ingredients, as they make
up the majority of the product. If the list contains overly processed ingredients, artificial additives, or
preservatives, it may be an indication that the product is not the healthiest choice. Look for products with
recognizable and whole-food ingredients for a more nutritious option.
Consider Allergens and Food Sensitivities
Food labels are also essential for individuals with allergies or food sensitivities. Manufacturers are required to
highlight common allergens, such as peanuts, soy, wheat, dairy, and shellfish. By carefully examining the labels,
you can avoid potential allergens and select products that suit your dietary restrictions or preferences.
Conclusion
Reading food labels is an indispensable skill for making healthier choices. By understanding the information
provided on the labels, you can evaluate the nutritional content, identify potential allergens, and make
well-informed decisions about the food you consume. Remember to pay attention to serving sizes, %DV, hidden sugars,
unhealthy fats, ingredient lists, and allergen information. With this knowledge, you can take control of your diet
and prioritize your health and well-being.