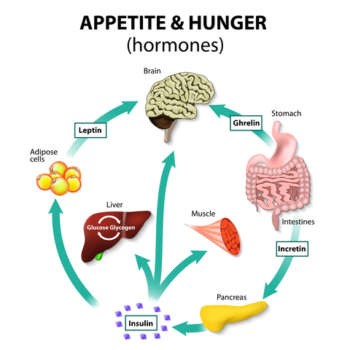
Metabolism plays a crucial role in weight control. It is the process through which our bodies convert the food we eat into energy. Understanding how metabolism works and the factors that influence it can help us make informed decisions about our diet and lifestyle to maintain a healthy weight.
Basics of Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the chemical reactions that occur in our bodies to sustain life. These reactions involve breaking down food and drink into energy, which is then used for various bodily functions such as breathing, digestion, and repairing cells. The speed at which our metabolism operates is known as metabolic rate.
Our metabolic rate is influenced by several factors:
Age: Metabolism tends to slow down with age, which can contribute to weight gain if dietary and activity levels remain constant.
Gender: Men generally have a higher metabolic rate than women due to differences in muscle mass and hormone levels.
Body composition: Muscle burns more calories at rest than fat, so individuals with a higher muscle mass tend to have a higher metabolic rate.
Physical activity: Regular exercise boosts metabolism and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Dietary patterns: The type and amount of food we eat can affect our metabolic rate. For example, consuming protein can temporarily boost metabolism, as it requires more energy to digest.
Metabolism and Weight Gain
When we consume more calories than we burn, our body stores the excess energy as fat, leading to weight gain. However, weight gain is not solely determined by metabolism; it also depends on lifestyle choices and overall energy balance.
Some medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism, can slow down metabolism and make weight loss more challenging. Conversely, certain medications or medical conditions, like hyperthyroidism, can increase metabolism, resulting in weight loss or difficulty gaining weight.
Metabolism Boosting Strategies
While we cannot control all aspects of our metabolism, there are certain strategies that can help boost our metabolic rate and facilitate weight control:
Exercise regularly: Engaging in both cardiovascular exercises and strength training can increase muscle mass and metabolic rate.
Eat a balanced diet: Consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can support a healthy metabolism.
Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water can help maintain metabolic functions.
Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal regulation, which may negatively affect metabolism.
Manage stress: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect metabolic rate. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga or meditation, can be beneficial.
Metabolism Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths surrounding metabolism and weight control that can be misleading. It is essential to separate facts from fiction when it comes to maintaining a healthy weight:
Eating small, frequent meals boosts metabolism: While frequent meals can help control hunger, the impact on metabolism is minimal. The total number of calories consumed throughout the day is more important.
Certain foods have negative calories: Some believe that certain foods require more calories to digest than they provide, leading to weight loss. However, this is not scientifically supported, as the energy expenditure during digestion is relatively small.
Metabolism slows down after dieting: While weight loss may temporarily lower metabolic rate, it is mainly due to a decrease in body mass. Regular physical activity and maintaining muscle mass can counteract this effect.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of metabolism in weight control empowers us to make informed choices regarding our diet and lifestyle. While we cannot control all aspects of our metabolic rate, adopting healthy habits such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding common misconceptions can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight.